|
|
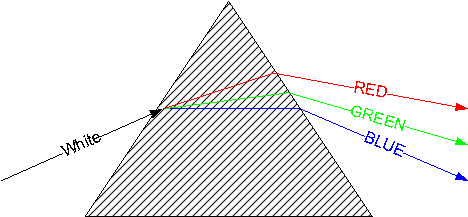
Equilateral dispersing prisms are used for wavelength separation
applications. The three sides are of equal length. A light ray is twice
refracted passing through the prism with total deviation denoted by
qd in the figure below. Deviation is a
function of refractive index, and hence wavelength. Angular dispersion
Dqd is the difference in deviation for
light rays having different wavelengths and varies with prism orientation.
- Reflection losses are minimized for un-polarized rays traveling parallel
to the base of the prism. This condition is called minimum deviation.
- Minimum deviation occurs when the ray and wavelength angle of incidence at
the entrance surface are equal to the angle of emergence (both angles measured
with respect to the surface normal).
- Antireflection coatings help reduce polarization at the prism surfaces by
increasing total transmittance.
General Specifications:
| Parameter |
Value |
| Material |
F2 glass |
| Dimension tolerance |
+/-0.2mm |
| Surface flatness |
l/2 |
| Angle tolerance |
+/-3 arc min |
| Surface quality |
60-40 |
| Coating |
Optional |
| PN |
Description |
Size |
Length |
Volume Price |
|
TRA010 |
Equilateral prism, F2, 10mm |
10 |
10 |
Request Volume
Quote |
|
TRA015 |
Equilateral prism, F2, 15mm |
15 |
15 |
Request Volume
Quote |
|
TRA020 |
Equilateral prism, F2, 20mm |
20 |
20 |
Request Volume
Quote |
|
TRA025 |
Equilateral prism, F2, 25mm |
25 |
25 |
Request Volume
Quote |
|
TRA030 |
Equilateral prism, F2, 30mm |
30 |
30 |
Request Volume
Quote |
|

